Get Healthy!
123 Results for search "Skin Disorders: Misc.".
Health News Results - 123
Women are two times more likely than men to die after receiving a combination of cancer immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors, but it's not clear if that difference is due to side effects or because the treatment isn't working, researchers say.
This new class of highly targeted drugs -- which includes pembrolizumab (Keytruda), nivolumab (Opdivo) or ipilimumab (Yervoy) -- has re...
- Ernie Mundell and Robert Preidt HealthDay Reporters
- |
- December 3, 2021
- |
- Full Page
When hair sprouts where you don't want it, you can always shave, but other ways to remove unwanted body hair can last longer.
The downside: Chemical hair removers can cause burning, itching or redness.
"Hair removal creams, lotions and gels are quick and easy to use, but they can sometimes irritate the skin," dermatologist Dr. Andrea Mabry said in an American Academy of Dermatology ...
- |
- September 19, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Parents: You may think temporary tattoos are harmless for children. But kids who decorate themselves with these transfer tattoos may be disrupting the skin's protective barrier, Spanish researchers report.
They looked at the effects on skin of permanent tattoos and temporary transfers. The surprising takeaway: Temporary transfer tattoos do more damage.
More moisture was lost in skin...
- Steven Reinberg
- |
- September 10, 2021
- |
- Full Page
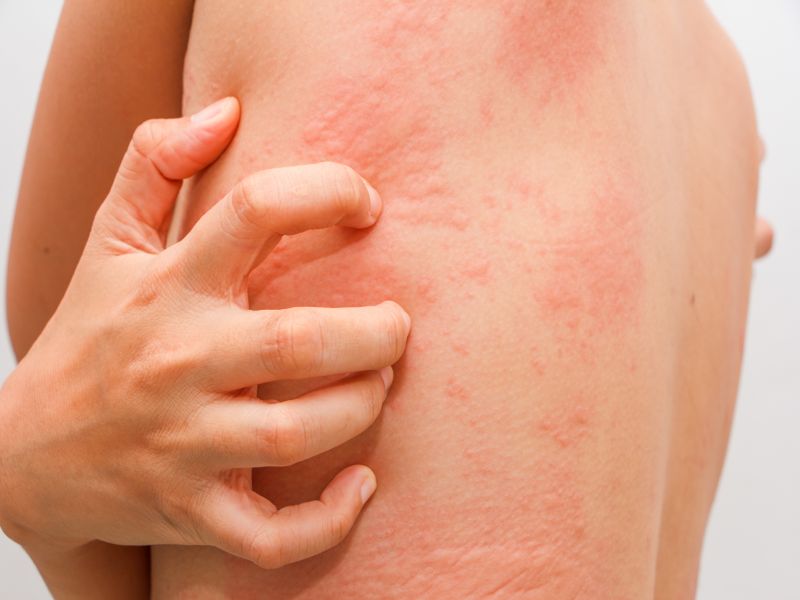
You've just bought a new skin care product and you're excited to see how it might transform your look. Instead, you end up with red, itchy or swollen patches because one of the ingredients causes an allergic reaction.
The best way to avoid this problem while trying something new is to test it on several small areas of your skin first to determine whether it's likely to irritate you, acco...
- |
- August 28, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Eating foods high in five key nutrients can help you have soft, glowing, healthy skin, an expert says.
Omega-3s: While they're typically associated with brain and heart health and lower blood pressure, they also "can reduce inflammation and keep your skin moisturized," clinical dietitian Margaret Ifarraguerri, of LifeBridge Health's Sinai Hospital of Baltimore, said in a ...
- |
- August 21, 2021
- |
- Full Page
An experimental gel has shown early promise in treating the most common form of skin cancer -- hinting at a potential alternative to surgery in the future.
Researchers tested the gel in 30 patients with basal cell carcinoma (BCC), a skin cancer diagnosed in more than 3 million Americans each year. The tumors rarely spread and are highly curable, usually through surgical removal.
Eve...
- Amy Norton HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 9, 2021
- |
- Full Page
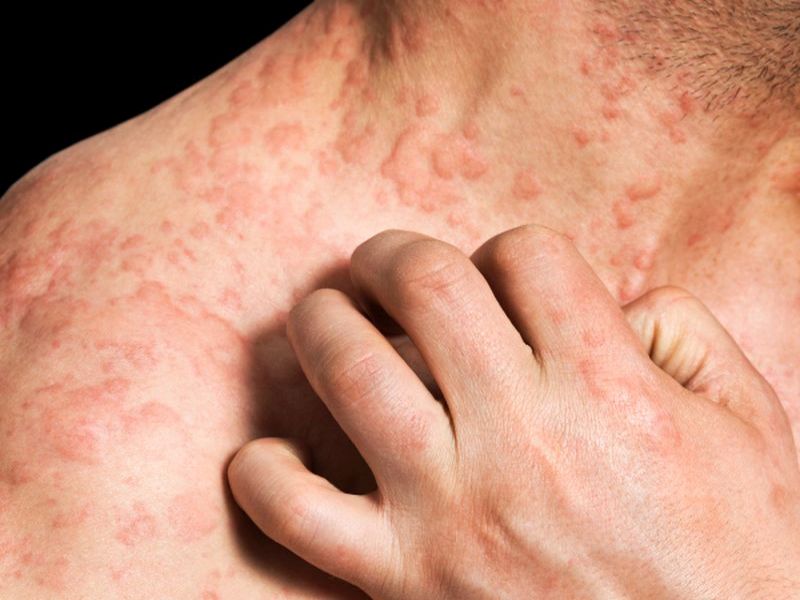
Rashes, itchiness and other skin problems can develop after people receive COVID-19 vaccines, but such problems are rare and go away quickly, new research shows.
For the study, the researchers looked at more than 40,000 employees of a Boston hospital system who received two-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccines (such as the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines) and completed at least one symptom survey after...
- |
- June 23, 2021
- |
- Full Page
An experimental antibody therapy may help ease skin symptoms from the autoimmune disease lupus, a small preliminary trial suggests.
Researchers found that a higher-dose version of the drug spurred a "clinically meaningful" symptom improvement for 87% of patients after one month.
But they also stressed that the findings are based on a small "phase 1" trial - a type of study designed ...
- Amy Norton HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 27, 2021
- |
- Full Page
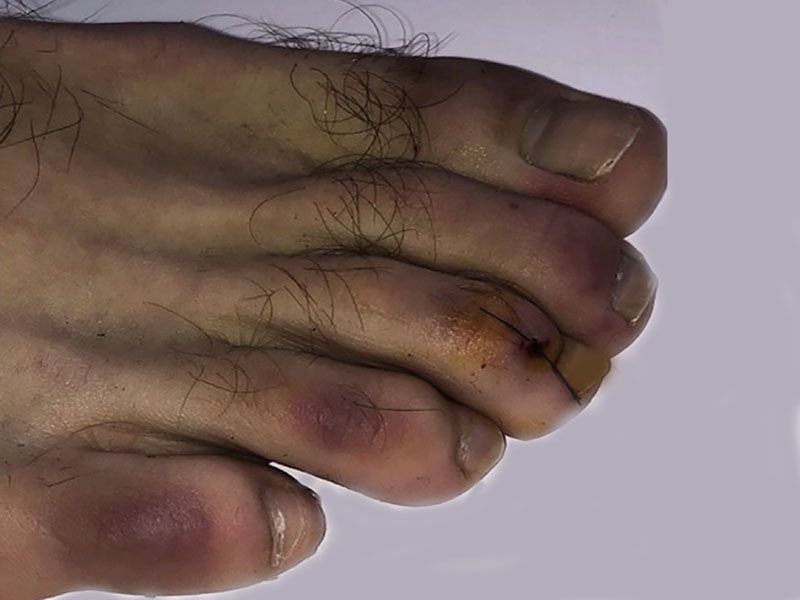
When checking your body for signs of skin cancer, don't overlook your nails.
The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) points out that skin cancer -- including melanoma, the deadliest type -- can develop under and around the fingernails and toenails. Though it's rare, it's more common in older people with darker skin.
Risk factors include personal or family history of melanoma or na...
- |
- May 16, 2021
- |
- Full Page
You might think everybody knows how to protect themselves from the sun's harmful rays, but a new survey reveals that one-third of Americans lack a basic understanding of sun safety and skin cancer.
That's the surprising takeaway from an American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) survey of 1,000 U.S. adults.
Fifty-three percent of respondents didn't realize shade offers protection from t...
- Cara Murez
- |
- May 4, 2021
- |
- Full Page
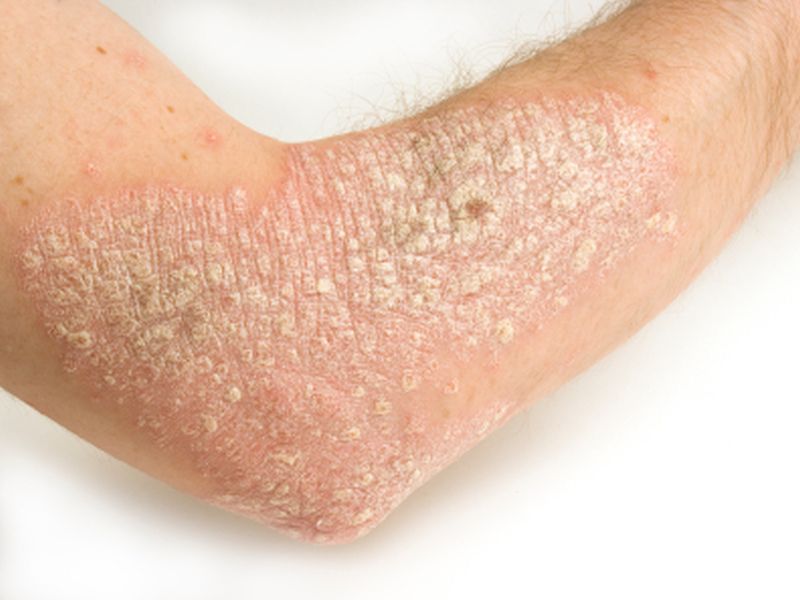
A breakthrough psoriasis drug is better at treating the itchy and painful skin disease than medicines already on the market, according to results from two clinical trials.
There was a "night and day difference" in the results from bimekizumab compared against two established psoriasis drugs, secukinumab (Cosentyx) and adalimumab (Humira), said Dr. Mark Lebwohl, a co-researcher in one of t...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- April 26, 2021
- |
- Full Page
When wildfires choked the air and turned the skies orange throughout the American West in recent years, they caused a variety of health problems from coughs and runny noses to life-threatening heart attacks and strokes.
But eczema and other skin issues were a result of the wildfires, too, according to researchers from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and the University ...
- Cara Murez
- |
- April 22, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Dermatologists liken skin to a window that can reveal what is going on inside the body, and a rash that sometimes follows a COVID-19 vaccine is one example.
When you get the shot, your immune system activates, preparing to recognize and fight off the virus in the future. This response and the inflammation that goes with it can occasionally result in a rash. But experts say as long as it h...
- Serena McNiff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- April 15, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Most people are familiar with common sun-protection advice, from wearing and reapplying sunscreen to putting on a hat.
But a new Canadian study finds that for people who take certain blood pressure medications, that advice becomes even more critical because those drugs can increase their sensitivity to the sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
The researchers reviewed data for nearly...
- Cara Murez HealthDay Reporter
- |
- April 12, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Once you've landed that coveted coronavirus vaccine appointment, you'll likely have to fill out a form on your medical history and whether you're allergic to any of the vaccine's ingredients. But there could be another question waiting for you: Have you ever had dermal filler injections?
That's because -- in rare cases -- people who've had the face-plumping injections can develop a mild, ...
- Serena McNiff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- April 12, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Millions of Americans have at some point in their lives gotten a long course of antibiotics to treat a bacterial infection. But according to new recommendations from a major U.S. doctors' group, some of the most common bacterial infections can now be treated with shorter courses of the drugs.
The advice, from the American College of Physicians (ACP), says that for several types of infec...
- Amy Norton HealthDay Reporter
- |
- April 6, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Some people given the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine may develop a reaction at the injection site that can first appear more than a week after they get the shot, research shows.
A minority of patients may experience a large, red, sometimes raised, itchy or painful skin reaction, according to researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston.
Although the reaction was seen in c...
- Steven Reinberg
- |
- March 4, 2021
- |
- Full Page
For people who have livedoid vasculopathy, which causes painful ulcers on the feet and lower legs, new research may bring newfound hope.
The disease is a rare medical mystery with no known cause and no commonly accepted cure, according to researchers who outlined the case of a single patient whose condition seems to have been relieved by a whole-foods, plant-based diet. The findings were ...
- Cara Murez
- |
- February 24, 2021
- |
- Full Page
More Asian and Hispanic people with lupus die prematurely than white patients, a new study reveals.
Death rates in San Francisco were nearly six times higher than expected among Hispanic patients with lupus and four times higher than expected among Asian women with lupus, the researchers found.
The higher death rate among racial and ethnic minority groups might result from more seve...
- Steven Reinberg HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 23, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Joe DiMeo's life changed forever when he fell asleep at the wheel on U.S. Route 22 in New Jersey on July 14, 2018.
The horrific crash left him with third-degree burns on 80% of his body and a grim prognosis.
Now, more than two years later, DiMeo, 22, is the recipient of the world's first successful double hand and face transplant, and on the road to recovery.
The historic surg...
- Denise Mann HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 3, 2021
- |
- Full Page
A majority of dermatology patients are happy with telehealth appointments in place of in-person office visits, a new study finds.
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced many medical specialties to move from in-person to online appointments, but dermatology had already seen increased use of telehealth visits over the last decade, according to the George Washington (GW) University researchers.
- Robert Preidt
- |
- February 3, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Dry and chapped lips are common during the winter, but there are a number of things you can do to protect them, an expert says.
"Cold, dry weather; sun damage; and frequently licking your lips are just some of the reasons your lips might feel dry and chapped this winter," dermatologist Dr. Noëlle Sherber said in an American Academy of Dermatology news release. "Understanding these causes...
- |
- January 30, 2021
- |
- Full Page
Add stress-related hair loss to the many problems caused by the coronavirus pandemic.
"I've had patients coming in recently with stress-related hair loss, who tell me they were so worried about dying earlier this year or even that they had COVID-19. But they don't see the effects until three months later," said dermatologist Dr. Ohara Aivaz of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
- Robert Preidt
- |
- November 20, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Black and Hispanic children in the United States have much higher rates of the skin condition eczema than white children, experts say.
These disparities in eczema -- also called atopic dermatitis (AD) -- will be presented at a virtual meeting of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), Friday through Sunday.
"Not only do Black children in the U.S. have signif...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- November 13, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Playing brain games before surgery may reduce your risk of delirium after your operation, a new study says.
Just as you can prepare your body for surgery, you can do the same for your brain by keeping it active and challenged through something called "neurobics," according to Ohio State University researchers.
Delirium -- a post-surgery complication especially common in older patien...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- November 13, 2020
- |
- Full Page
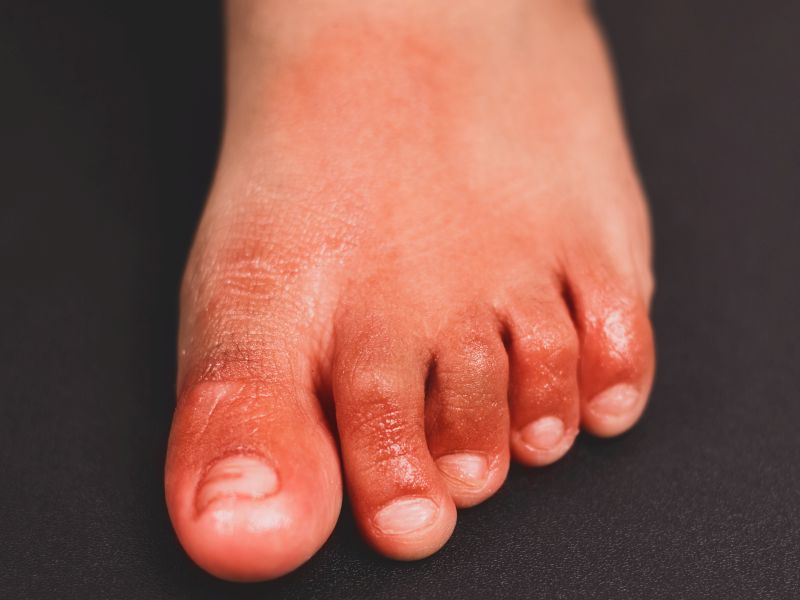
For some patients, COVID toes and rashes can last long after they recover from the coronavirus, a new study finds.
How often skin problems are linked to COVID-19 isn't known, but some patients -- so-called "long haulers" -- get better but don't appear to fully recover. For these patients, skin symptoms persist for 60 days or longer, according to researchers.
COVID toes and skin rash...
- Steven Reinberg
- |
- November 2, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Researchers in the United Kingdom have reassuring news for people with psoriasis based on the first analysis of a global registry of COVID-19 patients who also have the skin disease.
Moderate-to-severe cases of psoriasis are treated with drugs that suppress the immune system. This analysis of the international PsoProtect registry found that more than 90% of psoriasis patients surv...
- Cara Roberts Murez
- |
- October 27, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Proper skin care is crucial for cancer patients receiving radiation therapy, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) says.
Itchiness, redness, blistering and peeling are among the skin problems that radiation therapy can cause.
"During radiation therapy, the treated skin becomes very sensitive, which can cause painful rashes and delays in care," said dermatologist Dr. Anis...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- October 21, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Using your body as a canvas for tattoos might come at a price for your health.
New research suggests that all that ink impedes natural sweating -- and that might cause the body to overheat.
The study found that tattooed skin on arms "has reduced sweat rates, and thus potential heat loss capacity, during [whole-body heating], compared to adjacent skin without tattoos."
...- E.J. Mundell
- |
- September 30, 2020
- |
- Full Page
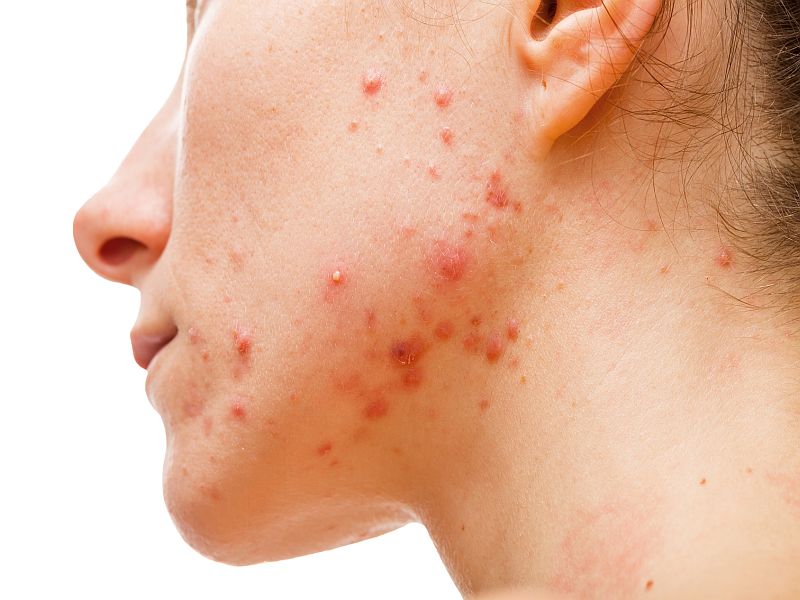
Dealing with acne can be especially difficult for people of color, a skin expert says.
Acne affects up to 50 million people in the United States each year. For people of color, acne is often accompanied by dark spots or patches called hyperpigmentation.
"Acne is the most common skin condition in the U.S., and it can be particularly frustrating for people with skin of color b...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- September 19, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Applying a type of "good" bacteria to the skin may relieve children of the itch and discomfort of eczema, a new, small study suggests.
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes dry, itchy skin and scaly rashes. It usually starts in early childhood, and commonly occurs along with allergies like hay fever and asthma, according to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and ...
- Amy Norton
- |
- September 15, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Biologic therapy for the skin condition psoriasis may reduce patients' risk of heart disease, new research suggests.
Chronic inflammation in people with psoriasis is associated with the development of plaque in heart arteries, which increases the risk of coronary artery disease. In biologic therapy, patients receive protein-based infusions to reduce inflammation.
"This is th...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- September 15, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Hand-washing is one of the best ways to prevent the spread of COVID-19 and other viruses, but for people with skin conditions like eczema, lathering up frequently can lead to dryness, cracking, itchiness, pain and even an infection.
If you're struggling to balance pandemic hand-washing and skin conditions, Dr. Jonathan Silverberg, a dermatologist at George Washington University School...
- Serena McNiff
- |
- August 21, 2020
- |
- Full Page
British scientists have discovered what makes people stink.
Blame an enzyme that hides in specific bacteria that colonize the human armpit.
"Solving the structure of this 'BO enzyme' has allowed us to pinpoint the molecular step inside certain bacteria that makes the odor molecules," said co-author Michelle Rudden. She's a postdoctoral research associate in biology at the ...
- Steven Reinberg
- |
- August 6, 2020
- |
- Full Page
A cream medication that eases skin inflammation might offer a safer treatment option for people with psoriasis, a new clinical trial suggests.
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects more than 8 million Americans, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation. The disease arises from an abnormal immune response that triggers rapid turnover of skin cells, causing them to pi...
- Amy Norton
- |
- July 15, 2020
- |
- Full Page
While rashes on the skin have long been tied to COVID-19, doctors in Spain report that rashes on the inside of the mouth are also occurring in some cases.
The rashes are clinically known as enanthem, and it's not surprising that they are showing up with COVID-19, said a U.S. dermatologist unconnected to the new study.
"An enanthem is a rash [small spots] on the mucous membra...
- E.J. Mundell
- |
- July 15, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Two new studies strongly suggest that the so-called "COVID toe" lesions that have popped up among some Americans during the pandemic may not be caused by infection with the new coronavirus after all.
Despite intensive testing over a wide time period, none of the 51 study patients afflicted with the reddened, tender toes came up positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19....
- E.J. Mundell
- |
- June 25, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Are you plagued by acne even though you're way past puberty? A new report might have you avoiding certain foods.
The study of more than 24,000 French adults found that sweet and greasy fare -- especially milk chocolate, sweetened drinks, dairy products, and sugary or fatty foods -- all appeared to raise the odds for zits.
The new findings "appear to support the hypothesis th...
- E.J. Mundell
- |
- June 11, 2020
- |
- Full Page
The virus that causes COVID-19 typically strikes the lungs with full force, but new research shows it can also cause frostbite-like patches on the hands and toes, and rashes on the body.
The condition has recently been dubbed "COVID toes." Fortunately, it isn't serious and the lesions usually disappear on their own, said Dr. Esther Freeman, director of Global Health Dermatology at Mas...
- Steven Reinberg
- |
- May 4, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Though most Americans are well aware that protecting themselves from sunburn is important, many don't take precautions, a new survey finds.
Protecting yourself from exposure to sunlight is the best way of preventing skin cancer, according to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD).
The results of the AAD survey show that 76% of Americans know the importance of sun pr...
- Steven Reinberg
- |
- May 2, 2020
- |
- Full Page
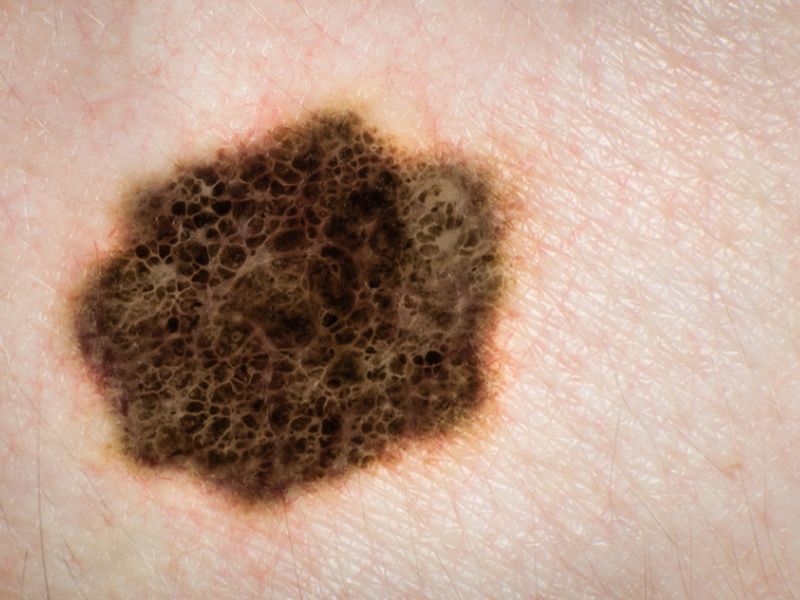
People whose spouse or partner has died are less likely to be diagnosed with melanoma, but more likely to die from it, a new study says.
An analysis of data from population-based studies conducted in the United Kingdom and Denmark between 1997 and 2017 found that people who had lost a spouse or partner were 12% less likely to be diagnosed with melanoma than others.
But b...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- March 6, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Skin rashes in people with lupus may have high levels of disease-causing bacteria that can spread to other people, according to a new study.
Researchers found that half of rashes in patients with lupus had abnormally high levels of Staphylococcus aureus (or staph), a common bacteria associated with skin infections.
That means "the person with the rash is a carrier for...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- February 28, 2020
- |
- Full Page
People sometimes refer to menopause as "the change of life," but many women are surprised that one of the things that changes is their skin, an expert says.
"Although fluctuating hormones during menopause can result in a number of skin changes, these don't need to be disruptive to daily life," said New York City dermatologist Dr. Diane Berson. "With the right care, women can continue ...
- Robert Preidt
- |
- February 23, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Burns on the face, arms and hands that require skin grafts. Acne boils and ugly rashes. Black hairy tongue and other oral lesions.
These are some of the ways that vaping can do serious damage to someone's skin, a new evidence review shows.
For example, an estimated 2,035 people with electronic cigarette burn injuries were treated in U.S. emergency rooms between 2015 and 201...
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- February 5, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Rubbing cream into your skin to calm an itchy rash may seem harmless, but not all topical anti-itch formulas are created equal.
"People don't understand the potential dangers of prescription-strength steroid creams," said Dr. Lawrence Green, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University in Washington, D.C.
Hydrocortisone -- a topical steroid often used to...
- Elizabeth Heubeck
- |
- January 23, 2020
- |
- Full Page
Skin creams and cosmetics can sometimes produce rashes instead of a beautiful complexion, but why has been a mystery until now.
A new study suggests that some chemicals in these products remove natural fats in skin cells, which might be why they trigger allergic reactions.
When the immune system spots something foreign, its T-cells spring into action, the researchers explai...
- Steven Reinberg
- |
- January 3, 2020
- |
- Full Page
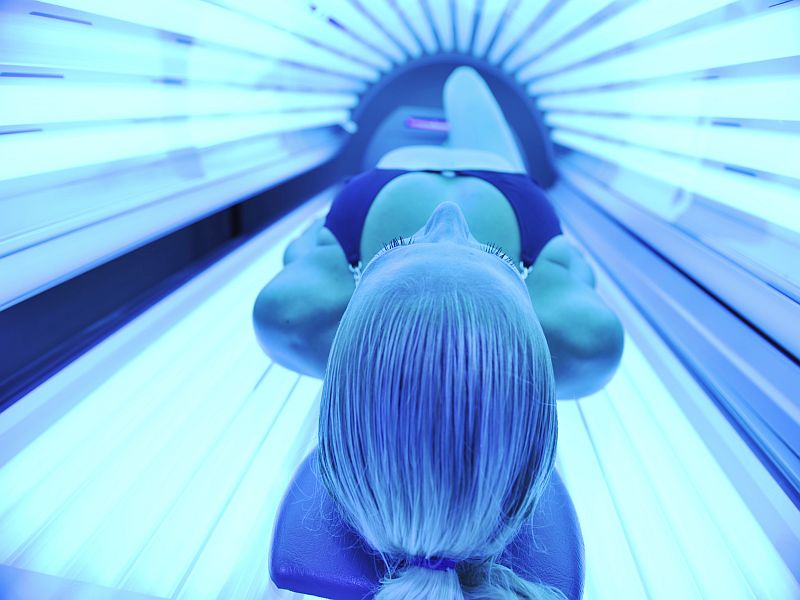
Widely condemned for driving up skin cancer risk, tanning beds remain common in that shrine to healthy living: gyms.
That's the finding from a study of tanning beds in three of America's six largest gym chains: Anytime Fitness, Planet Fitness and Gold's Gym.
Collectively, they operate more than 1,900 branches in the areas included in the study (33 states and Washington, D.C....
- Alan Mozes
- |
- December 23, 2019
- |
- Full Page
Stocking up on the latest beauty products can be costly. Is it possible to save money and still put your best face forward?
You may luck out and find things on sale at reputable retailers. But beware of prices that seem too good to be true on the internet or from sellers that may not be around tomorrow, like a flea market vendor.
Buy these products and you may end up with ...
- Serena Gordon
- |
- October 18, 2019
- |
- Full Page
Certain eating habits, high levels of stress and exposure to pollution are among the greatest factors associated with acne, researchers say.
They studied links to acne in more than 6,700 people from six countries in Europe and the Americas. The analysis showed that many more people with acne consume dairy products each day than those without acne -- 48.2% versus 38.8%.
...- Robert Preidt
- |
- October 11, 2019
- |
- Full Page
A new drug to treat chronic hives is producing solid results in clinical trials, and could be available to people suffering with the maddening itchy welts within a year or so, researchers say.
Ligelizumab works by targeting an immune system antibody called immunoglobulin E (IgE), which is responsible for the allergic reaction that causes hives, said lead researcher Dr. Marcus Maurer....
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- October 2, 2019
- |
- Full Page