Get Healthy!
Results for search "Brain".
Health Videos - 13
Health News Results - 454
A large new study suggests that higher levels of a common amino acid called tyrosine may be linked to a shorter lifespan in men.
The research, published recently in the journal Aging-US, examined whether blood levels of two amino acids, phenylalanine and tyrosine, were connected to how long people live.
Amino acids ...
- HealthDay Staff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 27, 2026
- |
- Full Page
Pregnancy Physically Alters A Woman's Brain – And A Second Pregnancy Even Moreso, Researchers Report
Pregnancy causes many profound changes to a woman’s body — and, it seems, her brain, according to a new study.
Pregnancy physically alters a woman’s brain, with a second pregnancy bringing even more profound effects, researchers reported Feb. 19 in the journal Nature Communications.
Repeated ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 23, 2026
- |
- Full Page
Imagine you’re driving down the street when, out of nowhere, a skateboarder rolls into your path.
You’re looking straight ahead, but can your brain spot the movement in your side vision fast enough for you to hit the brakes?
That split-second moment depends on something called visual processing speed, or how quickly your brain reacts to what’s happening around you,...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 10, 2026
- |
- Full Page
A parasite that lives inside as many as 1 in 3 people worldwide may be much harder to treat than once believed, according to new research from the University of California, Riverside.
The study, published Jan. 24 in the journal Nature Communications, found that Toxoplasma gondii hides inside the body in far...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 29, 2026
- |
- Full Page
Brain tumors are abnormal growths of cells in or around the brain. They can be primary (originating in the brain) or secondary (metastatic, spreading to the brain from cancer elsewhere).
They can also originate from the structures around the brain, like the dura (brain lining), the nerves or the bone of the skull. Not all brain tumors are cancerous.
Benign tumors typically grow m...
- Paul A. Gardner, MD, and Douglas Kondziolka, MD HealthDay Reporters
- |
- January 23, 2026
- |
- Full Page
The human brain may understand spoken language in a way that is surprisingly similar to how artificial intelligence (AI) processes words, a new study suggests.
By tracking brain activity as people listened to a spoken story, researchers found that the brain builds meaning step by step, very similar to the way large AI language models do.
The findings challenge older ideas that langu...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 22, 2026
- |
- Full Page
Ever notice how hard it is to stay sharp after a rough night of sleep?
A recent study published in the journal Nature Neuroscience points to a surprising reason why: The brain may briefly shift into a sleep-like cleaning mode, even while you’re awake.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of T...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 21, 2026
- |
- Full Page
The human brain is always working, reacting in a split second to dangerous events while slowly making sense of meaning, memories and decisions.
A new study from Rutgers Health explains how the brain pulls these fast and slow signals together to support thinking and behavior. The research was published recently in the journal
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 5, 2026
- |
- Full Page
Many Americans would rather pay more than negotiate, and new research suggests that’s exactly why “no-haggle” pricing works so well.
In five studies, researchers found that people avoid negotiating far more often than expected, even when cash is on the line.
“Across five studies, we found that 95% of individuals choose not to negotiate up to 51% of the time,&...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 5, 2026
- |
- Full Page
Sleep problems might be an early warning sign of dementia, a new study says.
Circadian rhythms that are weaker and more fragmented are tied to an increased risk of dementia, researchers reported Dec. 29 in the journal Neurology.
In fact, people with weak circadian rhythms have a more than doubled risk ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 2, 2026
- |
- Full Page
Think the good thoughts.
Manage stress.
Get your Zzzzzs.
And build a strong social support system.
New research shows that these factors — all of which are within your control — are powerful anti-aging tools.
"You can learn how to perceive stress differently," said study co-leader
Thinking about a positive moment with someone, even if it never happened, may actually make you like them more, new research shows.
A study published Dec. 10 in Nature Communications found that simply imagining a good interaction with a person can change your feelings toward them as well as how your brain s...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- December 11, 2025
- |
- Full Page
From childhood to old age, the human brain doesn’t just slowly fade or steadily grow, it changes in stages.
A new study suggests our brains go through four major turning points that shape how we think, learn and connect.
Researchers said those shifts happen around the ages of 9, 32, 66 and 83.
The findings, published Nov. 25 in the journal
Add one more malady to the potential risks from untreated sleep apnea: Parkinson’s disease.
A new study involving 11 million U.S. veterans finds that a person’s odds of developing
The brain is thought to be a sterile environment, free from germs.
But unexpected deposits of bacteria have been found inside brain tumors, apparently affecting how the cancers grow and behave, a new study says.
“This work opens a new dimension in our understanding of brain tumor biology,” senior researcher
Listening to your favorite singers may do more than lift your mood — it could also protect your brain.
A new study from Australian researchers found that older adults who regularly listened to music had a 39% lower risk of developing dementia compared to those who did...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- November 14, 2025
- |
- Full Page
If a healthy slurp is your aim, skip the banana when you whip up a smoothie.
Researchers at the University of California-Davis found that adding banana may interfere with absorption of powerful compounds called flavanols, which are linked to brain and heart health.
"We were really surprised to see how quickly adding a single banana decreased the level of flavanols in the smoothie an...
- Carole Tanzer Miller HealthDay Reporter
- |
- November 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Doctors think they’ve figured out a way to predict who might lose vision due to a high brain pressure disorder.
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) occurs when there’s unexplained pressure buildup in the fluid that cushions the brain in the skull, researchers explain in the journal Neurology
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 30, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Reality TV star, actress and mom Kim Kardashian, 45, disclosed in the season premiere of “The Kardashians” that a small aneurysm was detected in her brain.
An aneurysm occurs when a blood vessel wall weakens and stretches, creating a balloon or bubble. While aneurysms can appear anywhere, those in the brain, known as cerebral aneurysms, are likely more common than people reali...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 24, 2025
- |
- Full Page
If you need another reason to brush and floss, here it is: Research suggests keeping your mouth healthy might also protect your brain and heart.
Two new studies published Oct. 22 in Neurology Open Access linked gum disease and cavities to a higher risk of
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared another blood test that could help doctors identify whether a patient’s memory problems are likely caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
The new test, called Elecsys pTau181, was developed by...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 15, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A new study from Case Western Reserve University suggests a major shift in schizophrenia treatment: One that focuses on helping patients better interpret social cues.
“We’ve been treating schizophrenia with a one-size-fits-all approach for decades,” Jessica Wojtalik, an assistant...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 12, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A new study suggests there’s more to sleep than how long you snooze each night. Your overall sleep pattern could shape your mood, brain function and even long-term health.
Researchers from Concordia University in Montreal identified five distinct sleep profiles that may help explain why some people feel well-rested while others struggle with fatigue, poor focus or emotional ups and ...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A new gene therapy has shown promise in slowing the progression of Huntington’s disease, according to early trial results released Wednesday.
In a Phase 1/2 study, patients given a high dose of UniQure’s experimental therapy AMT-130 experienced a 75% slowing of disease progression after three years, the company said. The therapy also redu...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 26, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Skin-to-skin contact might help kick-start brain development in preterm babies, a new study says.
Preemies born before 32 weeks showed stronger development in brain regions tied to emotion and stress regulation if they received more skin-to-skin contact, researchers reported Sept. 24 in the journal Neurology...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 25, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A simple shunt can restore walking ability and independence in elderly people with a rare brain condition, a major new clinical trial has found.
Implanting a shunt to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid significantly improved walking and mobility among seniors with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), researchers reported Sept. 16 in
A new type of noninvasive brain stimulation may help people with moderate to severe depression feel better faster than standard treatments, researchers in a new report say.
The method, called high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS), uses small electrode...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 12, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Just like their human counterparts, cats may act cranky or confused and have trouble sleeping as they age.
They may even yowl more than usual at night.
These, researchers say, are dementia-like behaviors that may owe to an accumulation of plaques in their brain, just like those in people with
Talk therapy has the power to alter a person’s physical brain structure, a new study shows.
Psychotherapy caused measurable changes in the brains of people with severe depression, MRI scans revealed.
Specifically, most patients experienced growth in brain regions responsible for processing emotions,...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 27, 2025
- |
- Full Page
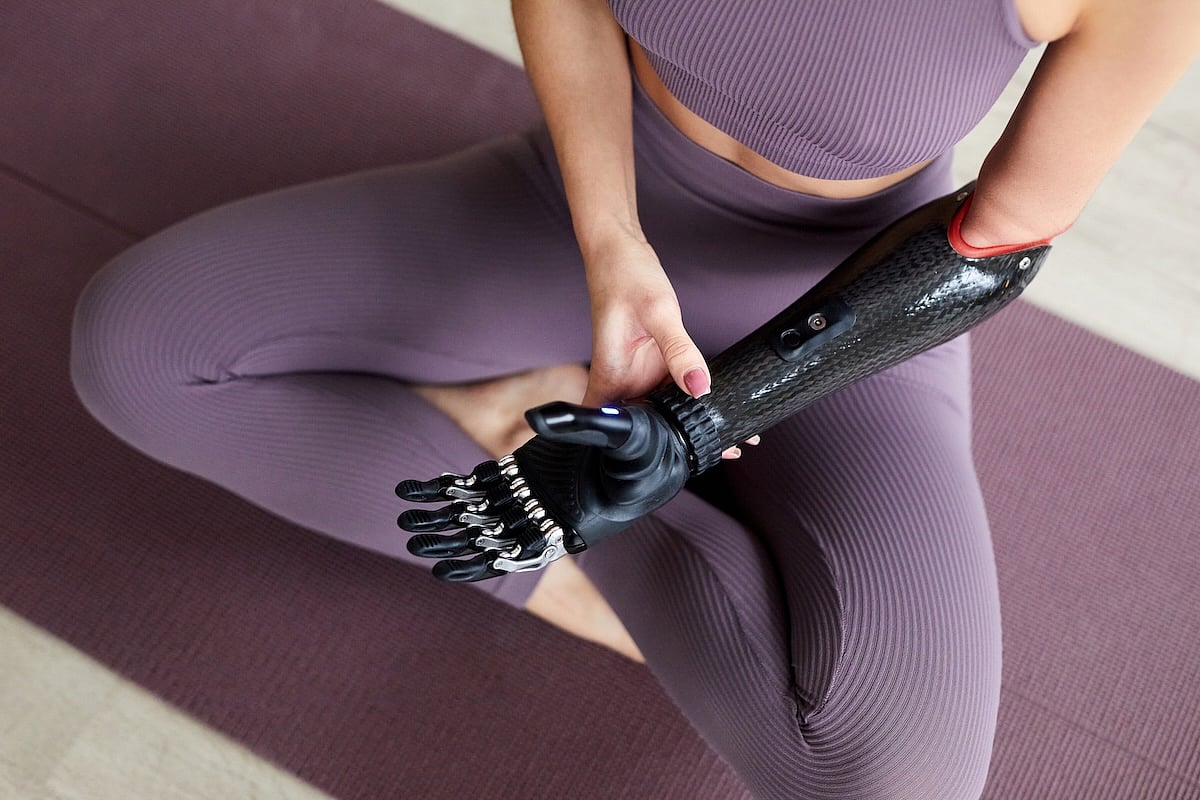
“Phantom limb” pain has been a curious aftereffect of amputation, with people experiencing false sensations from a hand, arm or leg that is no longer there.
Researchers now think they know why phantom limb sensations occur.
It turns out that the brain maintains a “map” of the body that remains unchanged even after a limb has been amputated, researchers report...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 25, 2025
- |
- Full Page
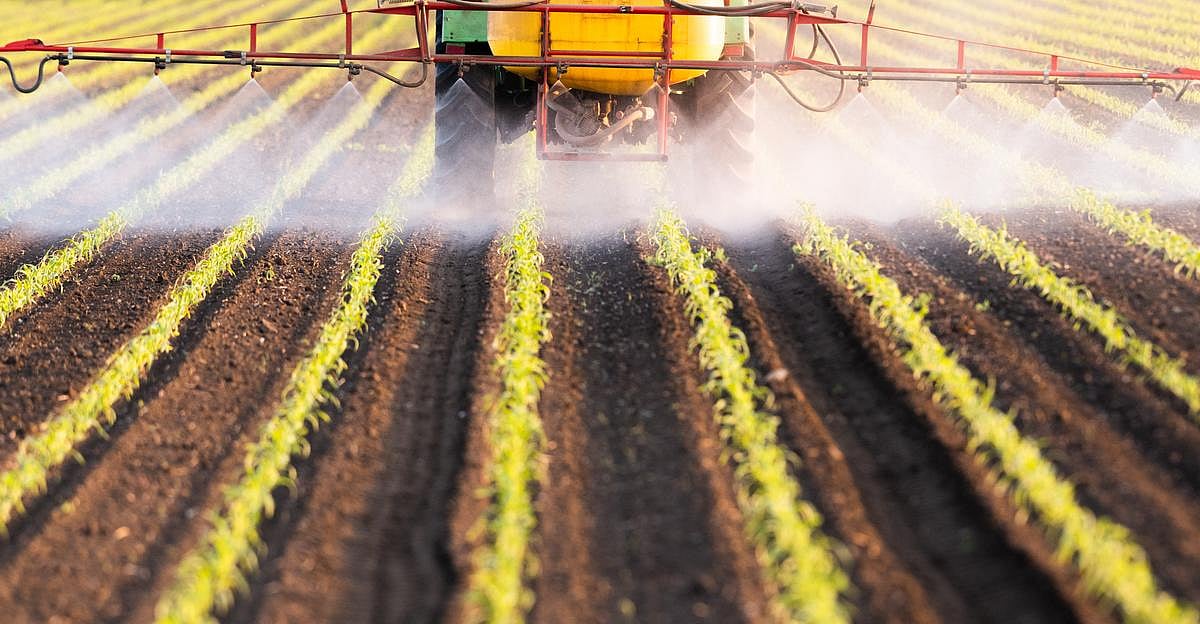
Exposure to a common pesticide during pregnancy can impair children’s brain development and motor function for years to come, a new study says.
The widely used pesticide chlorpyrifos (CPF) is linked to altered brain function and poorer fine motor control among children exposed to it while in the womb,...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 20, 2025
- |
- Full Page
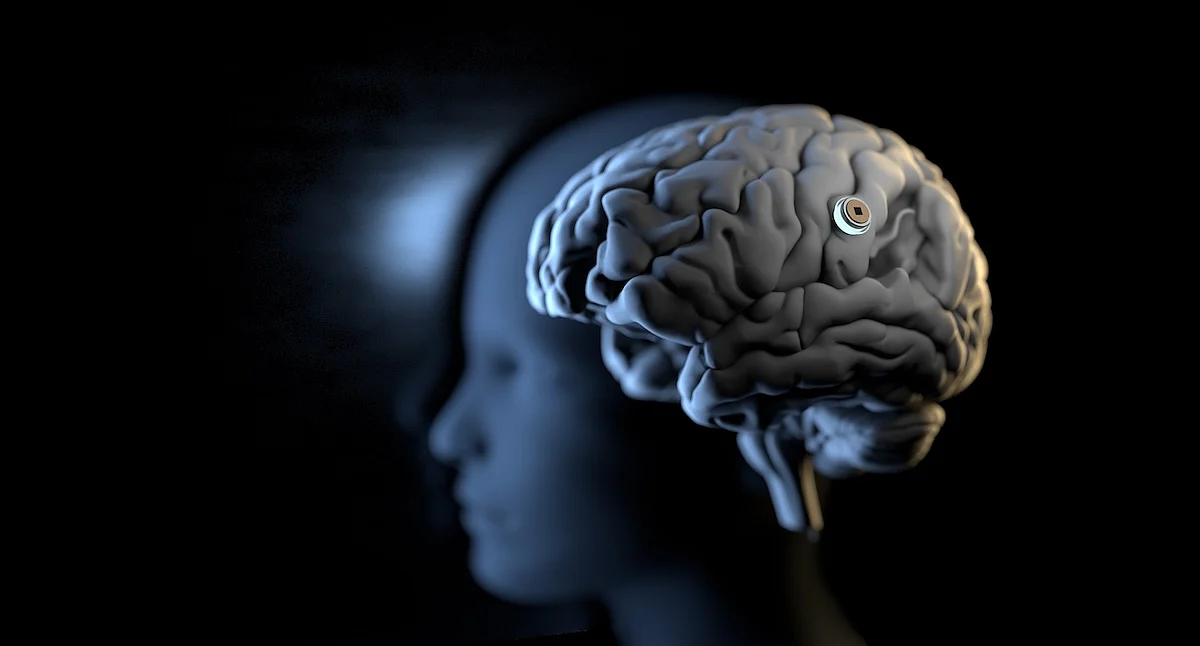
For the first time, scientists have created a brain implant that can “hear” and vocalize words a person is only imagining in their head.
The device, developed at Stanford University in California, could help people with severe paralysis communicate more easily, even if they can’t move their mouth to try to speak.
“This ...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 15, 2025
- |
- Full Page
An under-the-scalp implant can improve monitoring of a person’s epilepsy, giving doctors data they need to improve control over seizures, a new pilot study says.
Epilepsy patients must now keep a diary to track their symptoms.
But these self-observations are only right about half the time, researchers found when they compared patients’ diaries to tens of thousands of hou...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 14, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Tiny amounts of lithium — a natural metal — may help protect the brain from Alzheimer’s and signs of aging, new research shows.
Scientists at Harvard Medical School and Rush University found that when mice were fed a low-lithium diet,...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A 12-year-old South Carolina boy has died after being infected by a rare, brain-eating amoeba found in freshwater, his family’s lawyer said.
Middle school student Jaysen Carr died July 18 after swimming in Lake Murray, a large reservoir near Columbia, S.C., according to a
About 90,000 people are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease (PD) each year – one person every six minutes. While most people associate PD with tremors and stiffness, the condition is far more complex than these symptoms and may affect more than just movement.
An estimated 1 million people in the United States are living with this disease, according to the
Folks who breathe in more air pollution have a higher risk of developing a common non-cancerous brain tumor, a new study says.
Several different types of air pollutants, including particle pollution and nitrogen dioxide, appear to increase risk of meningiomas — tumors that form in the layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord, researchers reported July 9 in the journal <...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- July 10, 2025
- |
- Full Page
The first two years of a baby’s life are critical for brain development, and how the brain grows during that time may help predict future learning, behavior and health.
That’s according to experts at Cedars-Sinai, who are working to better understand how brain connections and genetics influence a child’s development.
“We want to use advanced imaging as a tool...
- HealthDay Reporter
- I. Edwards
- |
- June 21, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A Texas woman has died after using tap water in a sinus rinse, leading to a rare but often fatal brain infection, health officials report.
The 71-year-old woman died from a condition called primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), which is caused by a microscopic organism called Naegleria fowleri.
This brain-eating amoeba can live in warm freshwater and sometimes in untrea...
- HealthDay Reporter
- I. Edwards
- |
- June 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
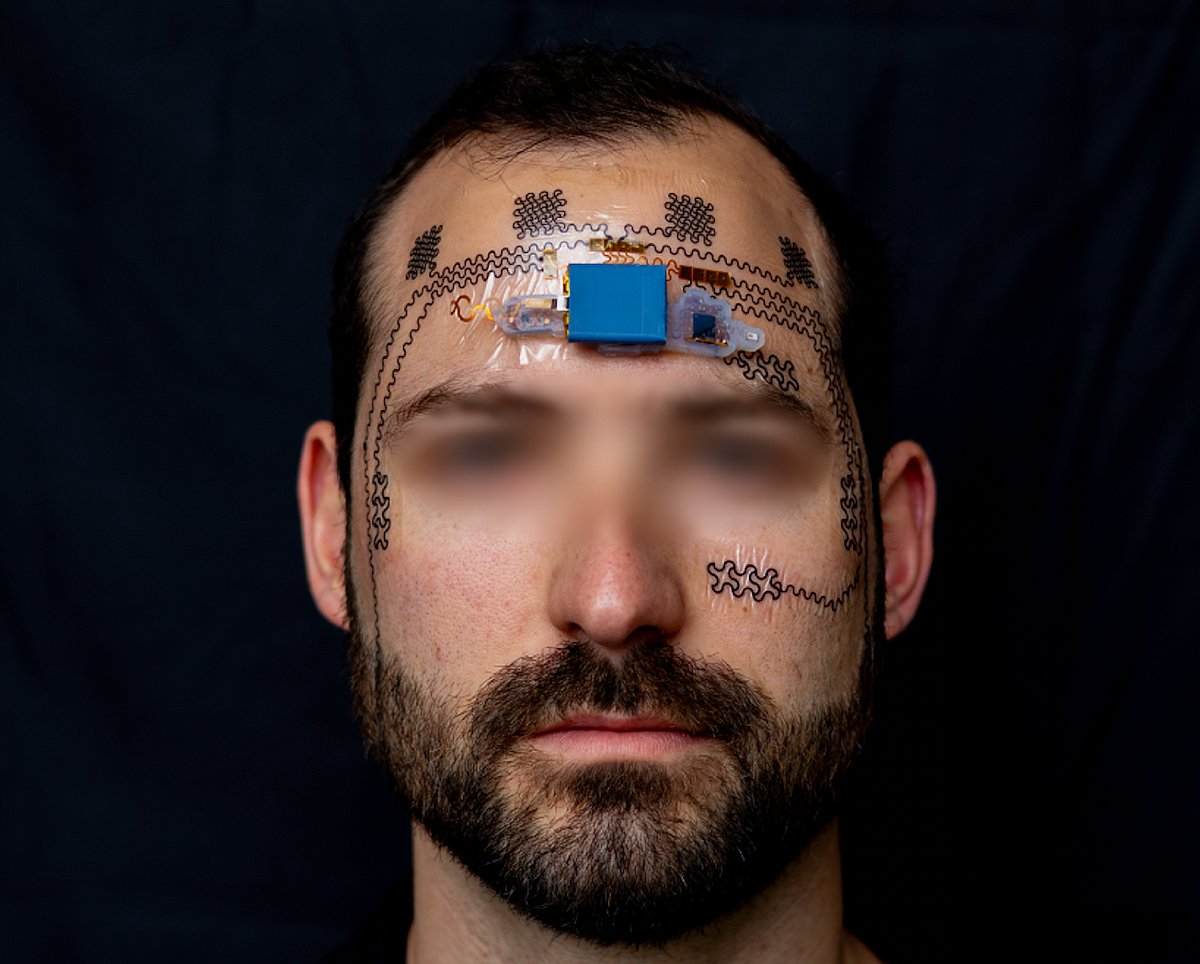
Ever thought so long and hard on a problem that your forehead grew hot, your brain became frazzled and your eyes grew bleary?
A new temporary tattoo can help measure that sort of mental strain, researchers report.
The wireless forehead electronic tattoo decodes brainwaves to measure mental strain and potential
Music legend Billy Joel has canceled tour dates through July 2026 after being diagnosed with a brain condition called normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH).
The 76-year-old singer announced Friday that his condition had worsened with recent performances, affecting his hearing, vision and balance, CBS News reported.
"I'm sincerely sorry to disappoint our audience, and thank yo...
- HealthDay Reporter
- I. Edwards
- |
- May 27, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) – known as Lou Gehrig’s Disease based on the iconic 1930s New York Yankee baseball player – is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects thousands of Americans every year. ALS remains one of the most complex and challenging disorders known to science.
May is ALS Awareness Month, making it an ideal time to take a closer look ...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Brian Lin, PhD, Research Portfolio Director at the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA)
- |
- May 3, 2025
- |
- Full Page
When a child tumbles to the floor from a blow to the head, a parent's inner alarms should sound. The child may have a brain injury.
Here's what parents need to know:
What is a concussion?
A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) that results from a direct hit to the head, face or neck.
Concussions may or may not involve a loss of consci...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Jeffrey Lo, MD, Attending Physician, Orthopedics and Sports Medicine Department, Boston Children's Hospital
- |
- April 20, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Health officials in Hood River County, Oregon, are investigating three cases of a rare and fatal brain disease known as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).
Two people in the county, which has a population of about 24,000, have died from the illness, and a third case is still being reviewed, Oregon Live reported.
CJD is caused by infectious proteins called prions. These p...
- HealthDay Reporter
- I. Edwards
- |
- April 14, 2025
- |
- Full Page
From slurping daily spoonfuls of fish oil to giving up alcohol, lifting weights and playing word games, older Americans think just about anything that might keep their brains sharp is worth a try.
After all, the risk of dementia -- a loss of memory, problem-solving and thinking abilities that often equals an end to independence -- rises sharply with age. By itself, the most common dementi...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Carole Tanzer Miller
- |
- April 12, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Common chemicals used in plastic and personal care products may interfere with brain development in babies, a new study says.
Phthalates are found in many everyday items, like food packaging, shampoo, toys and vinyl flooring.
They help make plastics soft and carry scents in products. But they may also harm unborn babies’ brains when mothers are exposed during pregnancy, resear...
- HealthDay Reporter
- I. Edwards
- |
- April 4, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Strokes caused by an artery tear are landing five times as many Americans in the hospital these days, a new study says.
Cervical artery dissection involves a small tear in the inner lining of an artery in the neck that supplies blood to the brain.
Blood can clot at the site of th...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- April 3, 2025
- |
- Full Page
For nearly two decades, a stroke had left a woman unable to speak -- until now.
Thanks to a new brain implant, her thoughts are being turned into real-time speech, giving her a voice again for the first time in 18 years.
The device was tested on a 47-year-old woman with quadriplegia who lost her ability to speak after a
Firefighters might face a higher risk of brain cancers caused by exposure to chemicals in fire extinguishers, a new small-scale study says.
Veteran firefighters appear to have a higher risk of brain tumors called gliomas, which can be caused by gene mutations linked to flame retardant chemi...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- March 11, 2025
- |
- Full Page
As this year’s severe flu season rages across the country, federal health officials are investigating a rise in rare but life-threatening brain complications in children.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says at least 19,000 people have died from the flu so far this w...
- HealthDay Reporter
- India Edwards
- |
- February 28, 2025
- |
- Full Page


















.jpg?w=1920&h=1080&mode=crop&crop=focalpoint)






























.jpg?w=1920&h=1080&mode=crop&crop=focalpoint)